The thermal conductivity of porous alumina ceramics prepared using different types of starch potato wheat corn and rice starch as pore forming agents has been investigated from room temperature up to 500 c.
Thermal confuctivity porous ceramics.
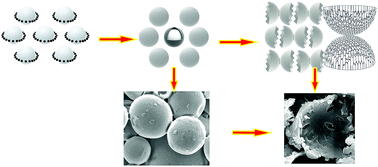
Starting with a commercial clay containing 75 kaolinite foams were made by mixing in water and methyl cellulose as a surfactant then beating.
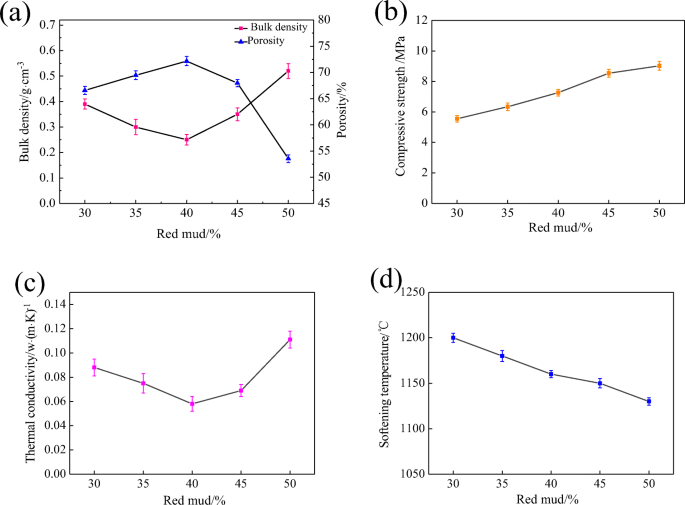
The compressive strength could be improved significantly by increasing the sintering temperature.
Zirconia and alumina are generally chosen as tbc top coat material.
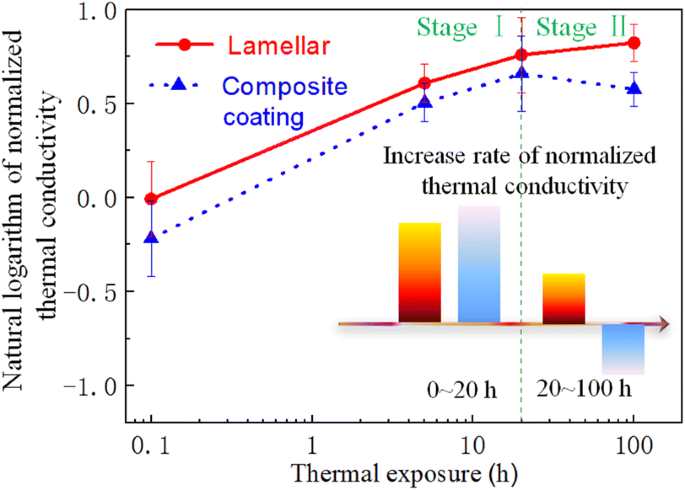
A toolbox of analytical relations is proposed to describe the effective thermal conductivity as a function of solid phase thermal conductivity pore thermal conductivity and pore volume fraction ν p.
The pore volume fraction was varied from 40 to 75.
The electrical resistivity of 100 cm is too high to be machined.
The thermal conductivity of porous alumina ceramics prepared using different types of starch potato wheat corn and rice starch as pore forming agents is investigated from room temperature up to 500 c.
Two sets of highly porous materials with different intrinsic thermal conductivity values for the solid skeleton were prepared.
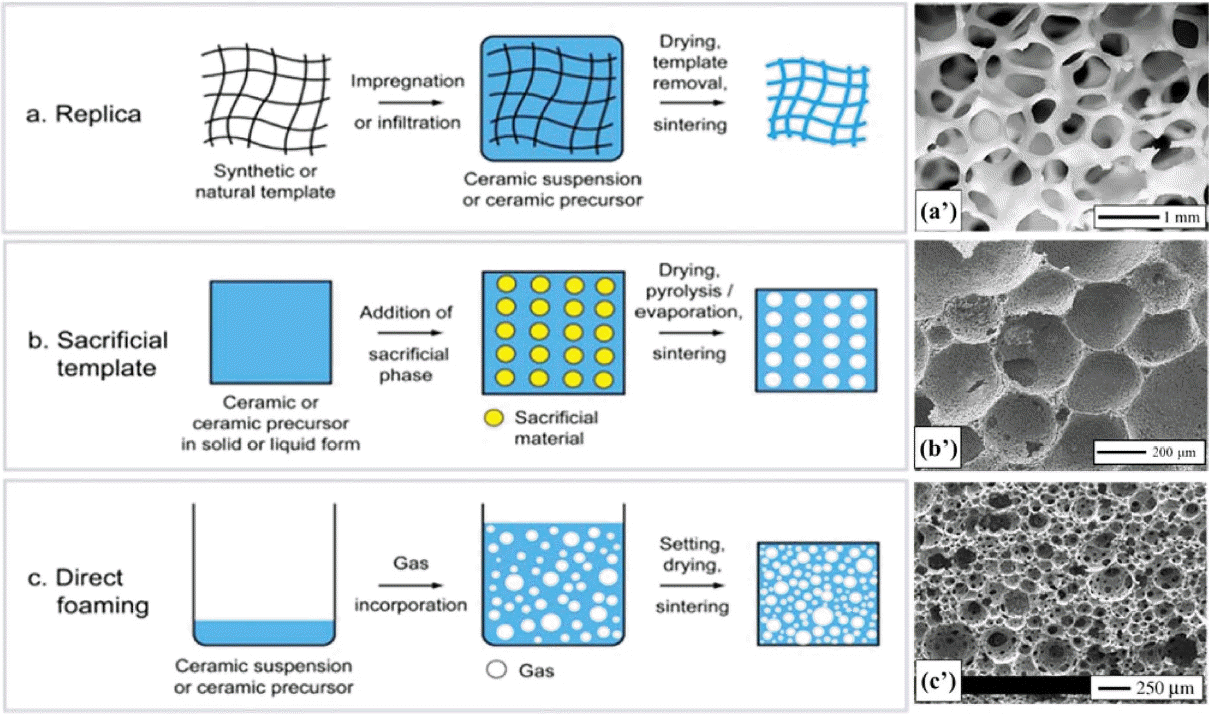
Porous ceramics were prepared by different methods to achieve pore volume fractions from 4 to 95.
Microstructural characterisation was performed including the determination of the pore size distribution psd.
Thus the reported thermal conductivity and electrical resistivity were 47 270w m k and 100 1011 cm respectively.
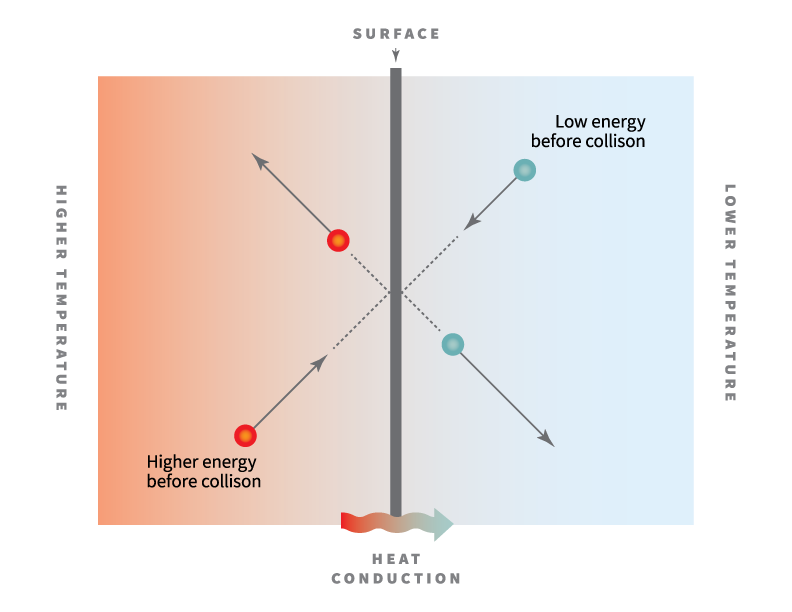
Gas pressure and temperature dependences of thermal conductivity of porous ceramic materials.
Ceramics have been developed by doping nitrogen into a sic lattice 7 however their thermal conductivity has not been reported.
In the present study the newly developed porous sic ceramics exhibited a very low thermal conductivity of 0 047 wm 1 k 1 at a high porosity 72 4 that is comparable to the thermal conductivity of sic aerogel 0 049 wm 1 k 1 and even lower than the thermal conductivity 0 068 wm 1 k 1 73 5 porous of a nano sic particle compact without heat treatment.
A clay based material exhibiting high pore volume fraction and low thermal conductivity suitable for thermal insulation is described.
Zirconia ceramic foams with porosity of 97 9 has low thermal conductivity of 0 027 0 004 w m k 1 which could be used as thermal insulation and refractory material.